You need to set aside an allowance for bad debts account to have a credit balance of $2,500 (5% of $50,000). When a business offers goods and services on credit, there’s always a risk of customers failing to pay their bills. The term bad debt refers to these outstanding bills that the business considers to be non-collectible after making multiple attempts at collection. Understanding how bad debt affects your taxes—and how to reduce future risk—can strengthen both your short-term cash flow and long-term financial strategy. This method records bad debt only when a specific invoice is deemed uncollectible. It’s straightforward but doesn’t follow the expense recognition principle, which makes it non-compliant with GAAP.
Accounting Jobs: Where to Start and What to Expect

As a result, the steps you’ll take to estimate your AFDA in this method are different compared to the percentage of sales method. If bad debt is becoming a concern for your business, we’ve got good news — there are several ways to get ahead of the problem. Modern accounting software can help you track payment patterns and flag potential issues early. These tools can show you which customers consistently pay late or have unpaid balances, helping you make informed decisions about extending credit. By providing transparent and detailed information, companies enhance the reliability and comparability of their financial statements.
- It’s a great way to visualize where your accounts receivable are piling up.
- Read on to learn more about the potential impact of widespread AI implementation from 2,355 senior business executives.
- Spend more time on calls, collecting from customers while we handle transcription & note-taking, boosting call volume & reducing past dues.
- The key to safeguarding your business from the pitfalls of bad debt lies in effectively managing your debts, as they often occur due to poor financial management.
- The good news is you can minimize bad debts by optimizing the way you manage your collections.
- By applying this percentage to the total credit sales for a period, companies can estimate their bad debt expense and adjust their allowance for doubtful accounts accordingly.
- In this guide, we’ll cover the essentials of bad debt expense and provide practical steps to reduce its effect on your business, ensuring stronger financial stability.
Seamless Integration with Your Accounting Software
- Companies periodically adjust their allowance for doubtful accounts to reflect the changing risk landscape and economic environment.
- The process is straightforward and allows you to write off the value of those outstanding invoices from your total taxable income on a case-by-case basis.
- A bad debt expense happens when customers don’t pay their bills, even after we try to collect.
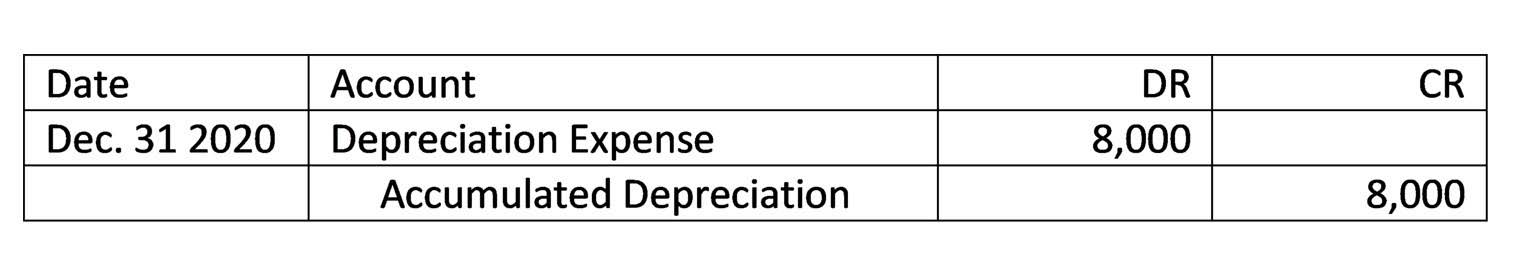
- This entry increases the bad debt expense and adjusts the allowance for doubtful accounts to reflect the new estimate.
- It is done based on probability by creating a provision or allowance for doubtful debts.
By improving how you manage credit and the money you’re owed, you minimize bad debts. Using advanced automation tools helps manage and track bad debts efficiently, giving you an up-to-date view of your finances. Listing bad debt expense under selling, general, and administrative expenses is a smart move. At the end of the accounting period, the business must recognize this $10,000 as a bad debt expense, reducing its https://www.bookstime.com/ reported income accordingly. In short, it is money owed to your business that you don’t expect to collect.
Historical Background
Accurate tracking of AR is essential for determining potential bad debts. By recognition of bad debts, the company’s assets or net income is not overstated or understated. Therefore, the true financial position of the company helps investors to decide about their investment decisions and stakes in the entity. For instance, in the one-year company had made a lot of credit sales hence increasing the net income. However, many debtors might become bad debt in the following year, putting pressure on the income statement. For instance, a retail supplier who offers Net 30 payment terms (e.g. they have 30 days to pay) may learn over time that a segment of customers simply never pay their invoices.
The allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra-asset account that reduces the gross accounts receivable balance. This entry adjusts the allowance for doubtful accounts to reflect the estimated uncollectible receivables based on the aging analysis. This entry records the bad debt expense and removes the QuickBooks uncollectible receivable from the accounts.


These expenses are recorded as a negative transaction on your business’s financial statements. A high bad debt ratio can indicate that a company’s credit and collections bad debt expense calculator policies are too lax, or it may suggest that the company is having trouble collecting customer payments. With B2B businesses relying on the credit model to bring in more clients and sales volume, bad debt has become an inevitable part of operations. Another method for estimating bad debt is through the utilization of the account receivable aging technique.

Can I deduct bad debt expense on my taxes?

Likewise, the calculation of bad debt expense this way gives a better result of matching expenses with sales revenue. In this article, we have tried to comprehend the accounting for doubtful and bad debts. Recording and recognition of bad debts and doubtful debts are very critical to the company’s financial position.
Deja una respuesta